营销型网站建设方案seo工资待遇怎么样
目录
Map
TreeMap
put()方法 :
get()方法 :
Set> entrySet() (重) :
foreach遍历 :
Set
哈希表
哈希冲突 :
冲突避免 :
冲突解决 ---- > 比散列(开放地址法) :
开散列 (链地址法 . 开链法)
简介 :
在Java中 , TreeSet 与 TreeMap 利用搜索树实现 Map 与 Set , 其实它们的底层就是一个红黑树(仅作了解).
HashSet与HashMap底层是Hash表.
关于搜索 :
Map和set是一种专门用来搜索的容器.其搜索的效率与其具体的实例化子类有关.
像我们之前常见的搜索方式有 :
1.直接遍历 , 时间复杂度为O(n) , 元素如果比较多那么效率就会很慢很慢.
2.二分查找, 时间复杂度为O(logn),但搜索前必须要求序列是有序的.
在现实中会有一些查找 : 例如
根据一个人的姓名去查找它的成绩,或者根据姓名去查找电话号码.
如果是这样的一些查找那么上述的两种方式就不太适合了,而Map和Set就是一种适合动态查找的集合容器.根据Map和Set我们就可去实现这种要求去查询.
Map
对于Map来说它是一个Key - Value 模型 Key 就是一个关键字 而Value就是Key对应的一种结果
例如 :
统计文件中每个单词出现的次数 , 那么Map就可以实现, <单词 , 单词出现的次数>
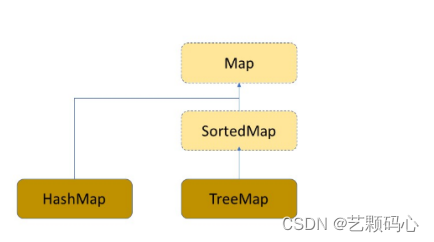
Map 与 SortedMap 是两个接口 , HashMap 与 TreeMap 就是两个普通类.
TreeMap
以下就是Map中的一些方法 :
put()方法 :
put方法的一些注意点 :
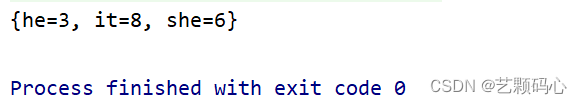
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();treeMap.put("he",3);treeMap.put("she",6);treeMap.put("it",8);System.out.println(treeMap);}
}
上面我们提到了TreeMap与TreeSet它的底层就是一个搜索树.在上一篇文章中我们讲到搜索树的原理以及是如何进行增,删,查的操作.

get()方法 :
根据get方法 : 当我们传进去一个Key关键字那么它就会输出相对应的value
public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();treeMap.put("he",3);treeMap.put("she",6);treeMap.put("it",8);Integer val = treeMap.get("he");System.out.println(val);}
如果treeMap对象中不存在所要查找的关键字Key时 , 则会返回一个null.

或者我们可以使用另一个方法 :
如果treeMap对象中不存在abc这个字符串时 , 则输出默认值10.
public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();treeMap.put("he",3);Integer val = treeMap.getOrDefault("abc",10);System.out.println(val);}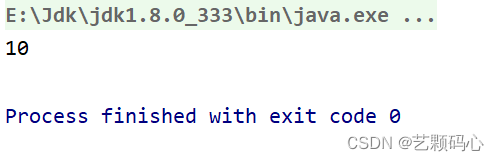
KeySet()方法 :
将treeMap对象中全部key放入keySet中.
public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();treeMap.put("he",3);treeMap.put("she",6);treeMap.put("it",8);Set<String> keySet = treeMap.keySet();System.out.println(keySet);}
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() (重) :
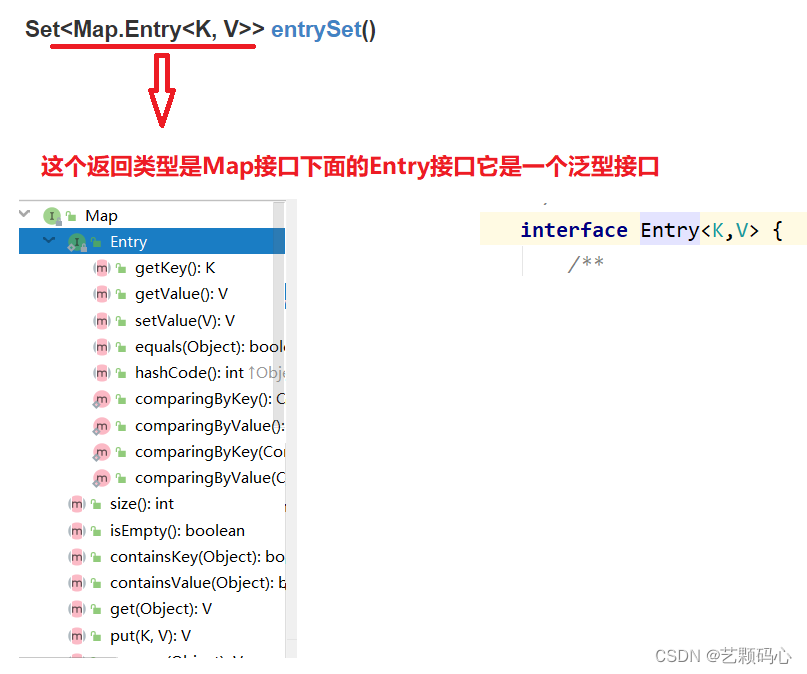
这个方法它会将所有存在treeMao对象中的Key - Value 模型返回.
public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();treeMap.put("he",3);treeMap.put("she",6);treeMap.put("it",8);Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entry = treeMap.entrySet();System.out.println(entry);}
foreach遍历 :
我们就可以使用Entry里面的getKey()方法来得到每一个模型的关键字key :
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry: set) {System.out.print(entry.getKey() + " ");
}
注意 :
1.Map是一个接口,不能直接实例化对象, 如果要实例化对象只能实例化其实现类TreeMap或者HashMap.
2.Map中存放的键值对的Key是唯一的,value是可以重复的
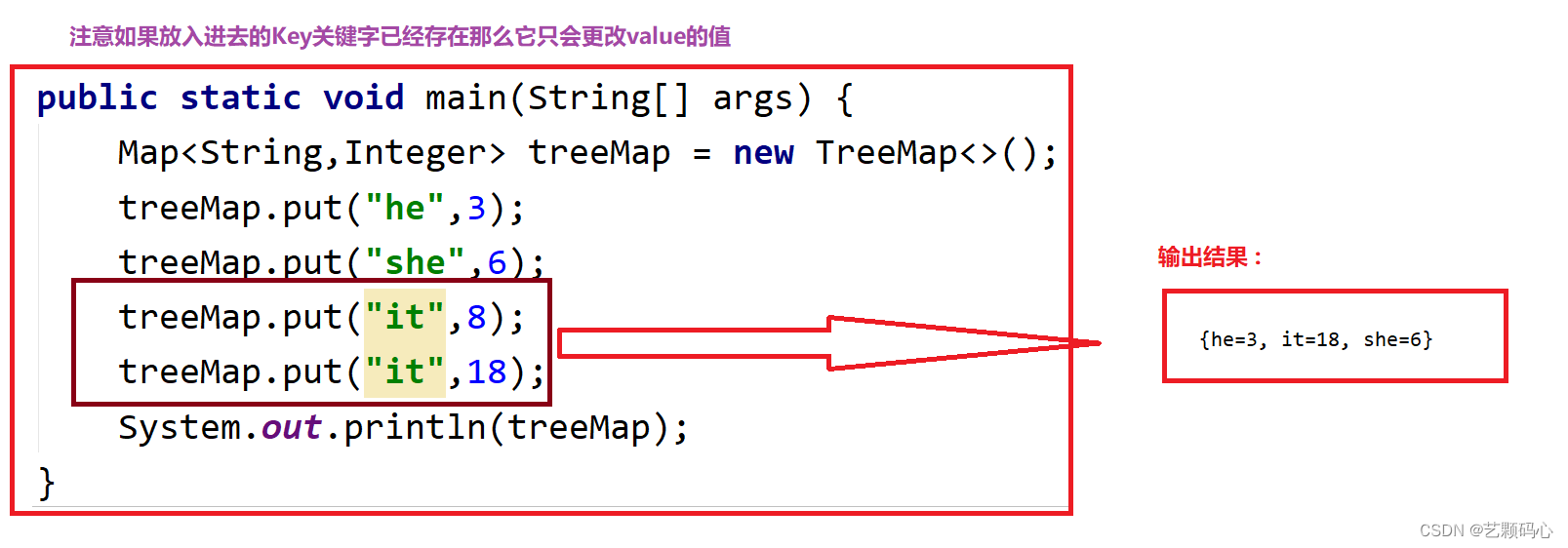
3 . 在TreeMap中插入键值对时,key不能为空,否则就会抛NullPointerException异常,value可以为空。但是HashMap的key和value都可以为空。

使用Collection<V> values()方法
Set
Set是一个纯Key模型. 因此它只存关键词key.
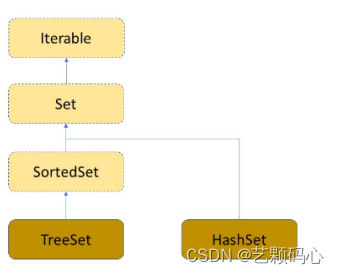
Set 与 SortedSet 就是两个接口 , 而 TreeSet 和 HashSet是两个普通类.
TreeSet使用add的方法来添加Key.但是如果重复它就不放入.
public static void main(String[] args) {Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();set.add("she");set.add("he");set.add("he");System.out.println(set);}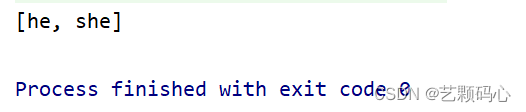
TreeSet底层也是去调用TreeMap.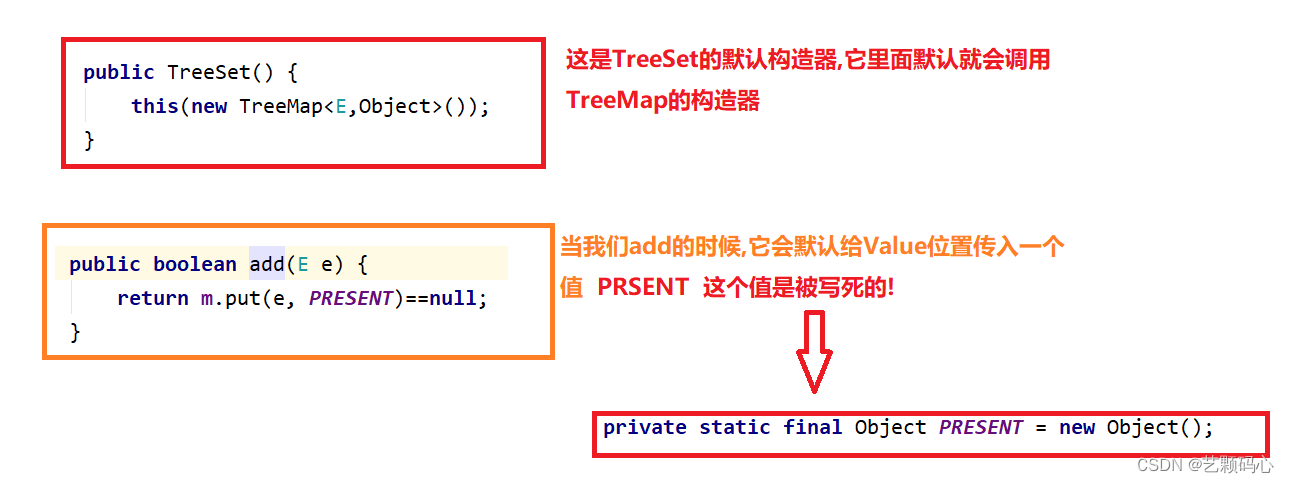
注意 :
哈希表
在顺序结构以及平衡树中, 查找一个元素时,必须要经过关键码的多次比较.顺序查找时间复杂度O(n),平衡树中为树的高度,即O(logn).
而哈希表它就可以直接以O(1)的速度去查找!!!!
实现方法 : 构造一种存储结构 , 通过某种函数使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立---映射关系,那么在查找时通过该函数就可以很快找到该元素.
哈希函数 (散列函数) : 哈希方法中使用的转换函数称为哈希(散列)函数 , 构造出来的结构称为哈希表(HashTable)(或者称散列表)
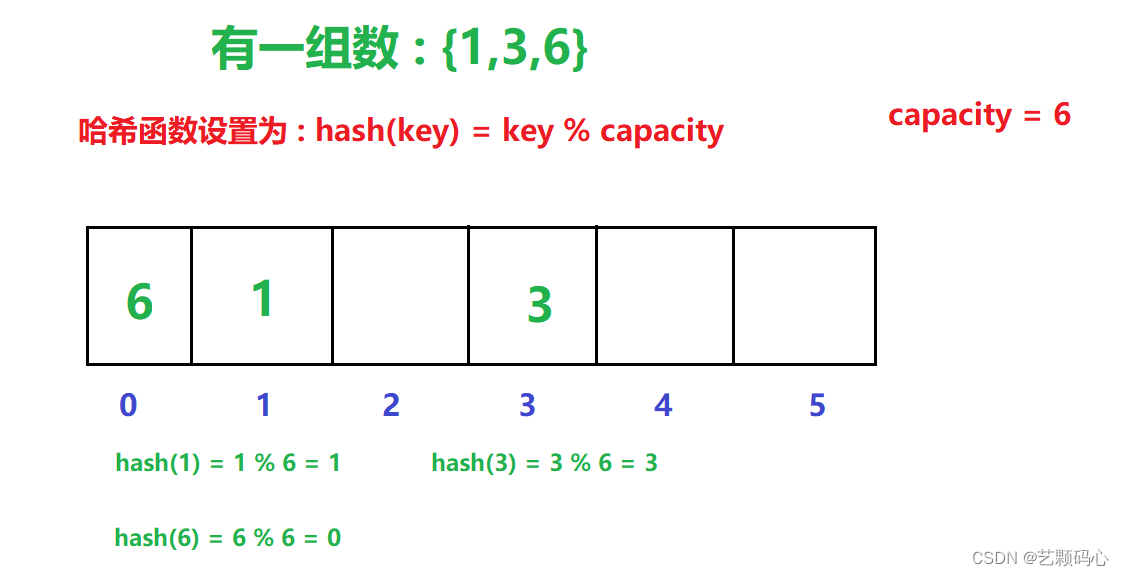
例如 : 有一组数 {1,4,3,2,75,23}
哈希函数设置为 : hash(key) = key % capacity ; capacity为元素底层空间总的大小
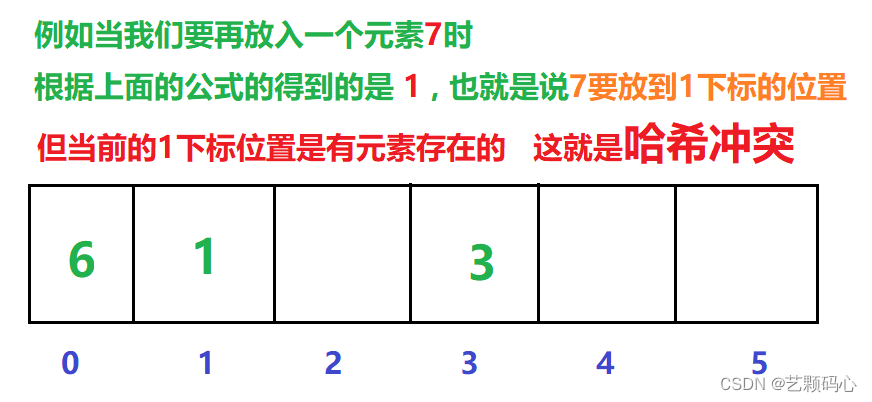
哈希冲突 :
冲突避免 :
首先我们要明白一点 : 在哈希表底层数组的容量往往是小于实际要存储的关键字的数量的, 这就导致了 : 冲突的发生是必然的 , 因此我们要做的就是尽量的降低冲突率.
冲突避免 -----> 负载因子调节 (重点)
散列表的载荷因子定义为 : α = 填入表中的元素个数 / 散列表的长度

冲突解决的两种方法 :
冲突解决 ---- > 比散列(开放地址法) :
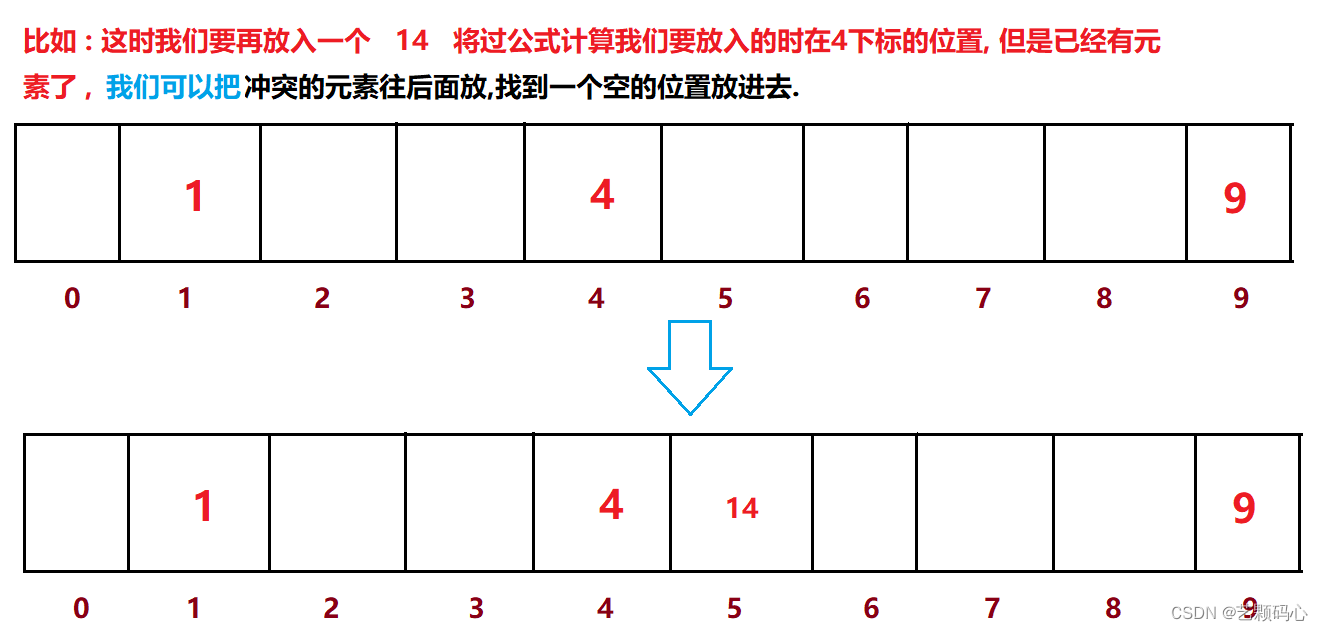
上面这种方法叫做线性探测 : 缺点是如果我们要删除4下标这个元素,如果直接删掉之后,那14就找不到了,因此我们在删4的时候只能是通过标记法来标记他已经被删除.
相比起比散列, 开散列会好很多
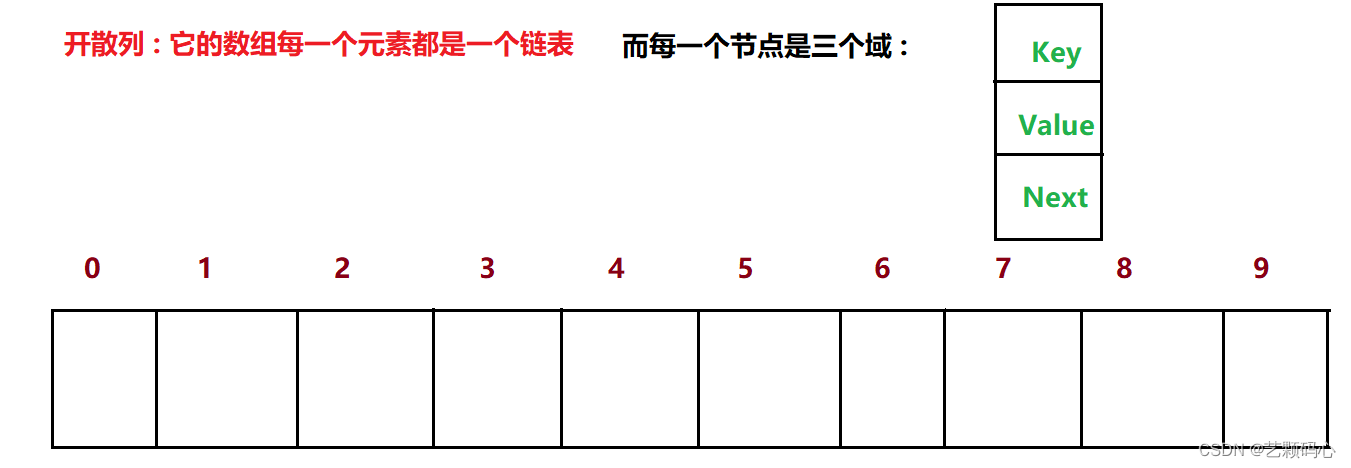
开散列 (链地址法 . 开链法):
它是由数组 + 链表 + 红黑树 组织起来的
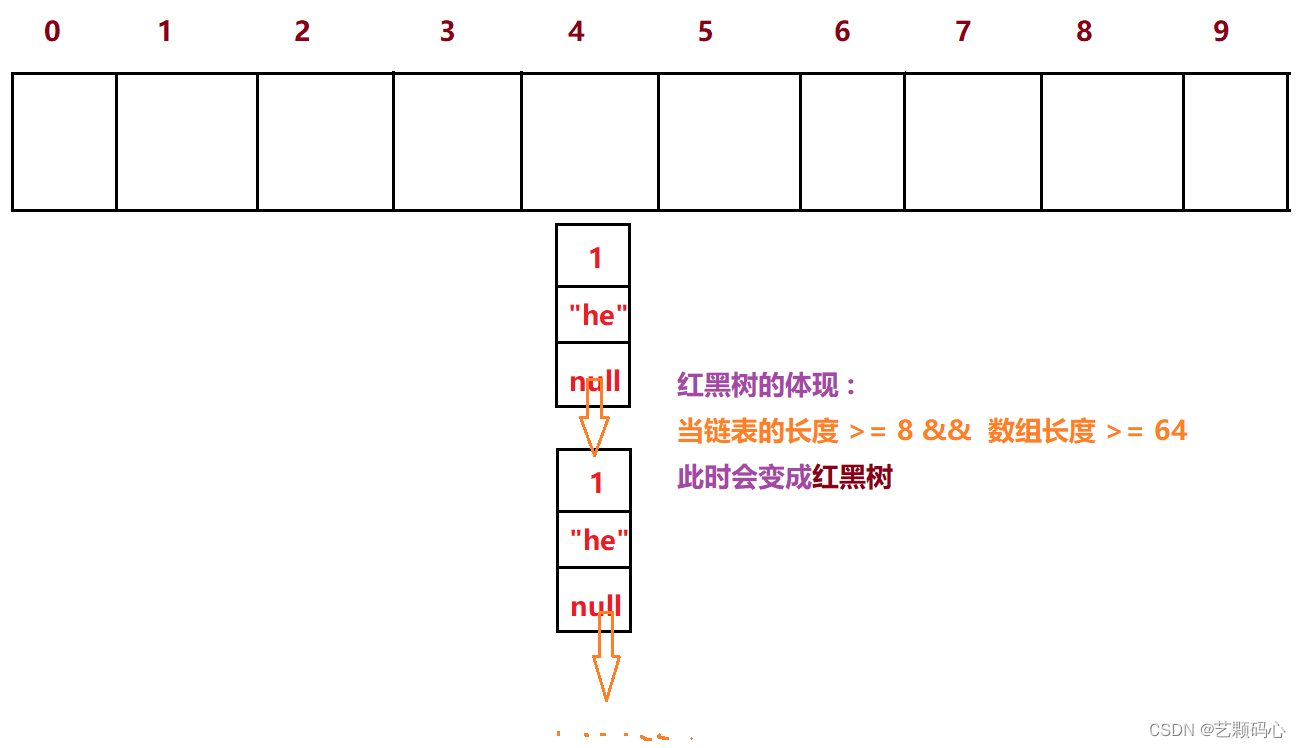
红黑树的体现 :
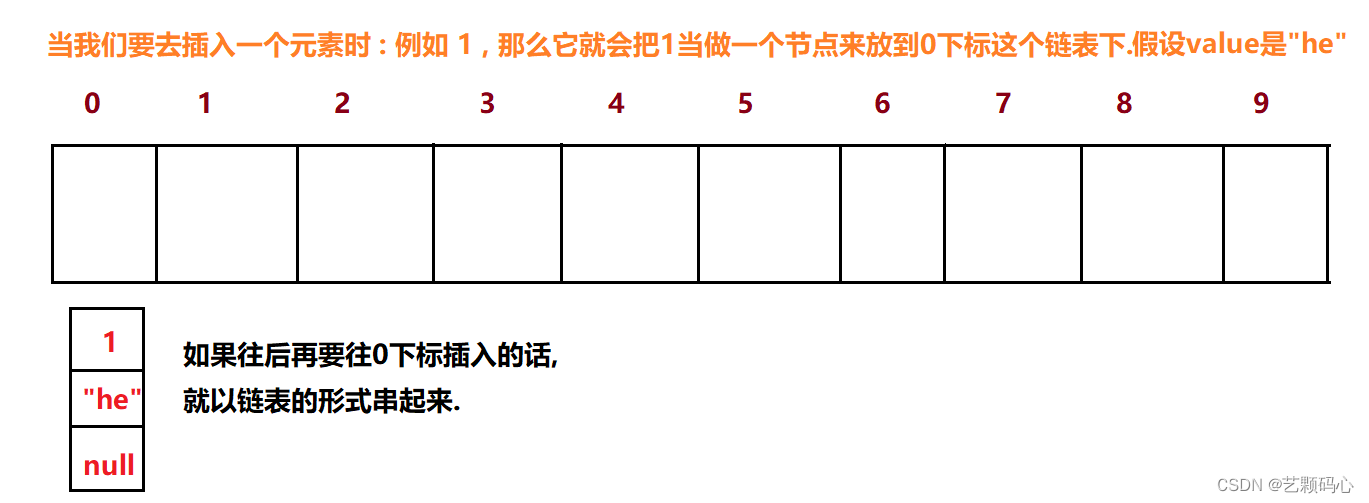
在java底层代码中 , 每一个下标下是一个链表, 采用的是尾插.
接下来我们来实现一下哈希表下面的put方法 :
我采用了头插的方式.
public class HashBuck {static class Node {public int key;public int val;public Node next;public Node(int key, int value) {this.key = key;this.val = value;}}public Node[] array;public int usedSize;//负载因子 设置为0.7public static final double loadFactor = 0.7;public HashBuck() {this.array = new Node[10];}public void put(int key, int val) {int index = key % array.length;Node cur = array[index];while (cur != null) {if (cur.key == key) {cur.val = val;}cur = cur.next;}Node newNode = new Node(key,val);newNode.next = array[index];array[index] = newNode;usedSize++;//如果负载因子 大于0.7那就扩容数组if (calculateLoadFactor() >= loadFactor) {//扩容}}//计算负载因子public double calculateLoadFactor() {return (usedSize*1.0) / array.length;}}重点在于 : 如果负载因子超过了0.7,那么我们就要去扩容,
扩容要注意 :
一定要重新哈希计算,假设我们最开始的14存在了4下标,扩容后它应该在14下标.
//扩容private void resize() {Node[] newArray = new Node[2*array.length];for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {Node cur = array[i];Node curNext = null;while (cur != null) {curNext = cur.next;int index = cur.key % newArray.length; //找到了在新数组当中的位置cur.next = newArray[index];newArray[index] = cur;cur = curNext;}}this.array = newArray;}get方法 :
public int get(int key) {int index = key % array.length;Node cur = array[index];while (cur != null) {if (cur.key == key) {return cur.val;}cur = cur.next;}return -1;}我们在去求哈希参数的位置时 , 用key%数组的长度. 但是如果key是引用类型呢?
那我们就去调用hashcode方法 , 如果引用数据类型没有实现hashcode方法,那么就会调用Object里面的hashcode方法.
class Student {public int age;public String name;public Student(int age, String name) {this.age = age;this.name = name;}
}
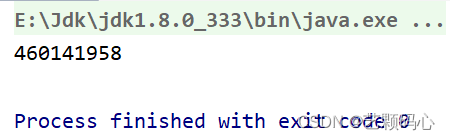
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Student stu = new Student(12,"zs");System.out.println(stu.hashCode());}
}
但是问题又来了 : 如果stu 与 stu2里面的两个参数值一样 , 按照我们的理解它们应该是一样的 :
但结果确实不一样的两个结果.
public static void main(String[] args) {Student stu = new Student(12,"zs");System.out.println(stu.hashCode());Student stu2 = new Student(12,"zs");System.out.println(stu2.hashCode());}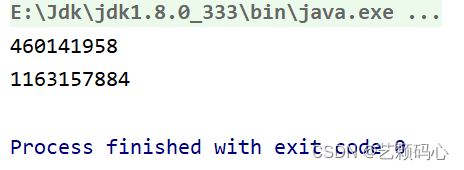
要想解决这个问题 , 我们就去Student里面去重写hashCode方法.
class Student {public int age;public String name;public Student(int age, String name) {this.age = age;this.name = name;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return age == student.age &&Objects.equals(name, student.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(age, name);}
}可以看到重写后的哈希方法里 , return语句 括号里面有两个参数 , 也就意味着根据age与name去形成结果. 因此在一样的age 与 name 的情况下 , 它们调用hashCode返回的值都是相同的.
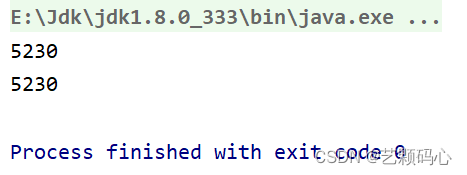
将上面的代码转变为引用类型 :
package demo2;public class HashBuck<K,V> {static class Node<K,V> {public K key;public V value;public Node<K,V> next;public Node(K key, V value) {this.key = key;this.value = value;}}public Node<K,V>[] array;public int usedSize;public static final double loadFactor = 0.7;public HashBuck() {this.array = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[10];}public void put(K key, V value) {int index = key.hashCode() % array.length;Node<K,V> cur = array[index];while (cur != null) {if (cur.key.equals(key)) {cur.value = value;return;}cur = cur.next;}Node<K,V> node = new Node<>(key,value);node.next = array[index];array[index] = node;usedSize++;if (calculateLoadFactor() >= loadFactor) {resize();}}private void resize() {Node<K,V>[] newArray = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[2*array.length];for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {Node cur = array[i];Node curNext = null;while (cur != null) {curNext = cur.next;int index = cur.key.hashCode() % newArray.length; //找到了在新数组当中的位置cur.next = newArray[index];newArray[index] = cur;cur = curNext;}}this.array = newArray;}public double calculateLoadFactor() {return (usedSize*1.0) / array.length;}public V get(K key) {int index = key.hashCode() % array.length;Node<K,V> cur = array[index];while (cur != null) {if (cur.key.equals(key)) {return cur.value;}cur = cur.next;}throw new RuntimeException("找不到Key所对应的Value");}
}
重点要注意一下 : 在求哈希函数时 , 要用key.hashCode() % 数组的长度. 再然后引用数据类型之间比较相不相同要用equals()方法.
问题 : hashCode()一样 , equals一定一样吗 ?
equals()一样 , hashCode()一定一样吗 ?
答案分别为 : 不一定 , 一定 .
以上就是我对 HashMap 与 HashSet 的一些见解 . 希望可以帮到大家~~~
